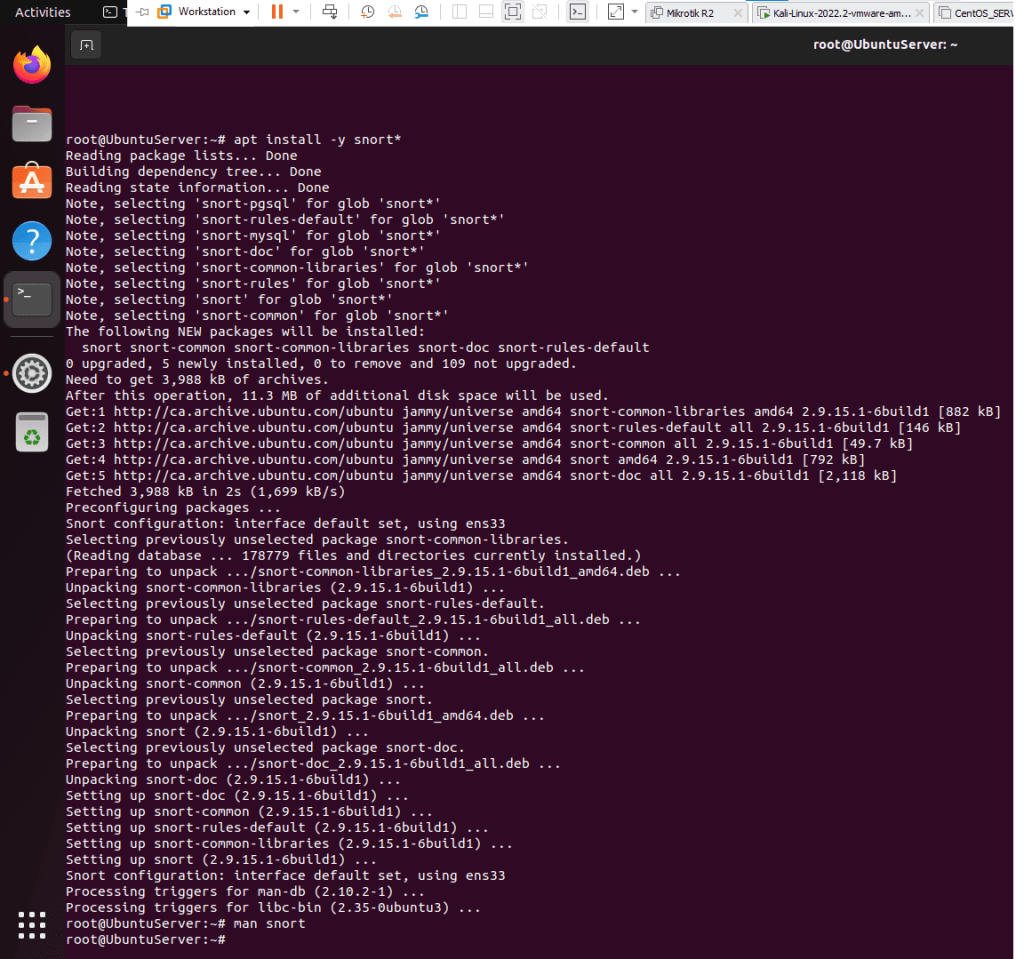
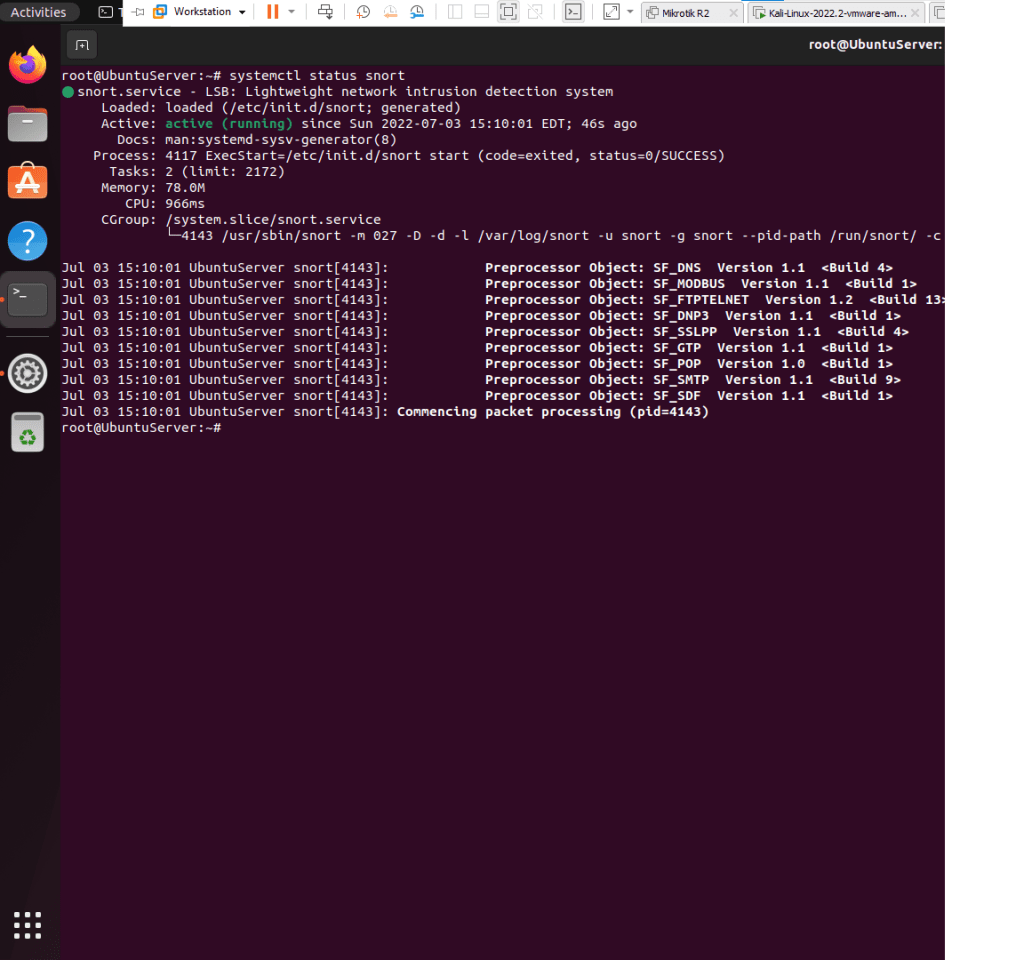
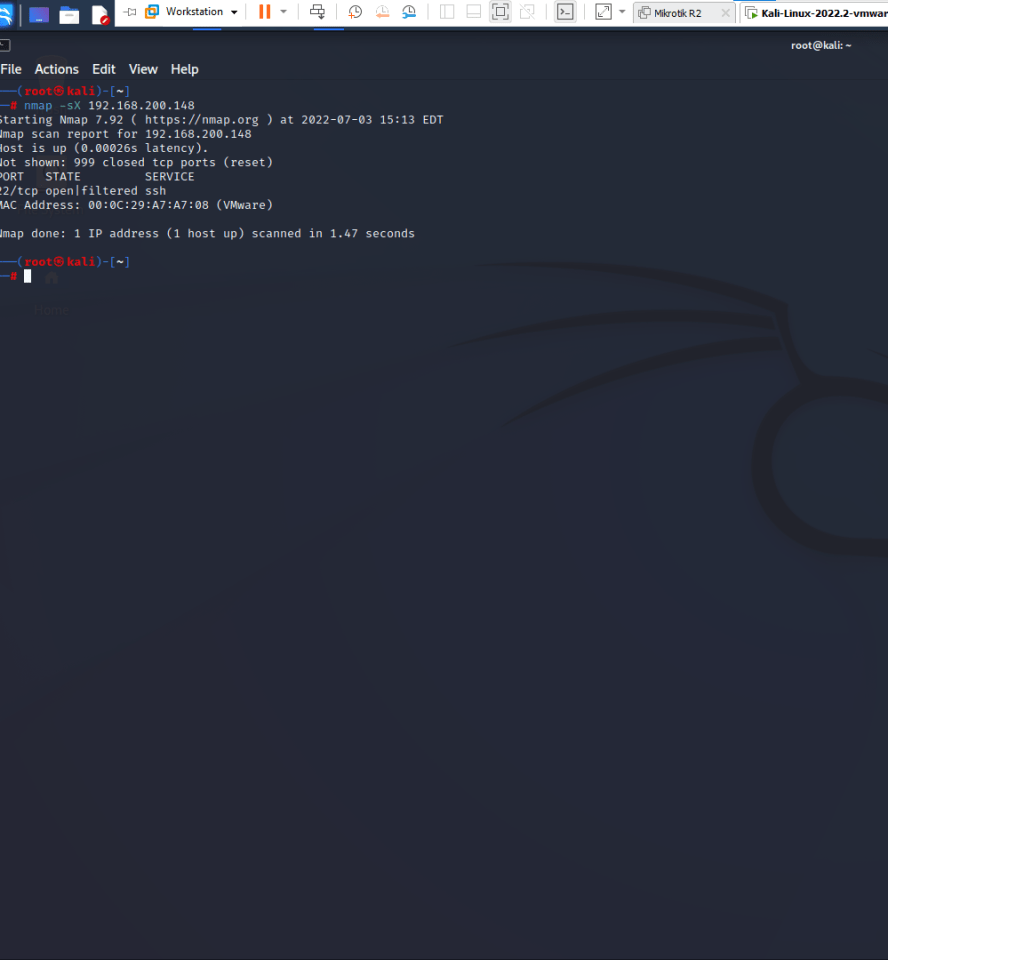
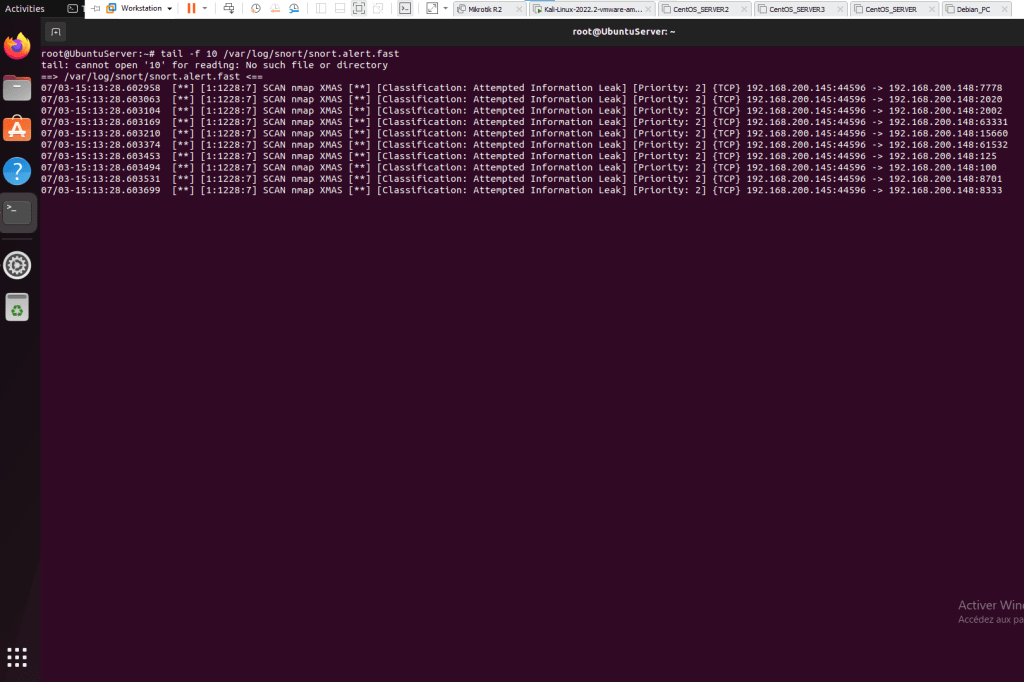
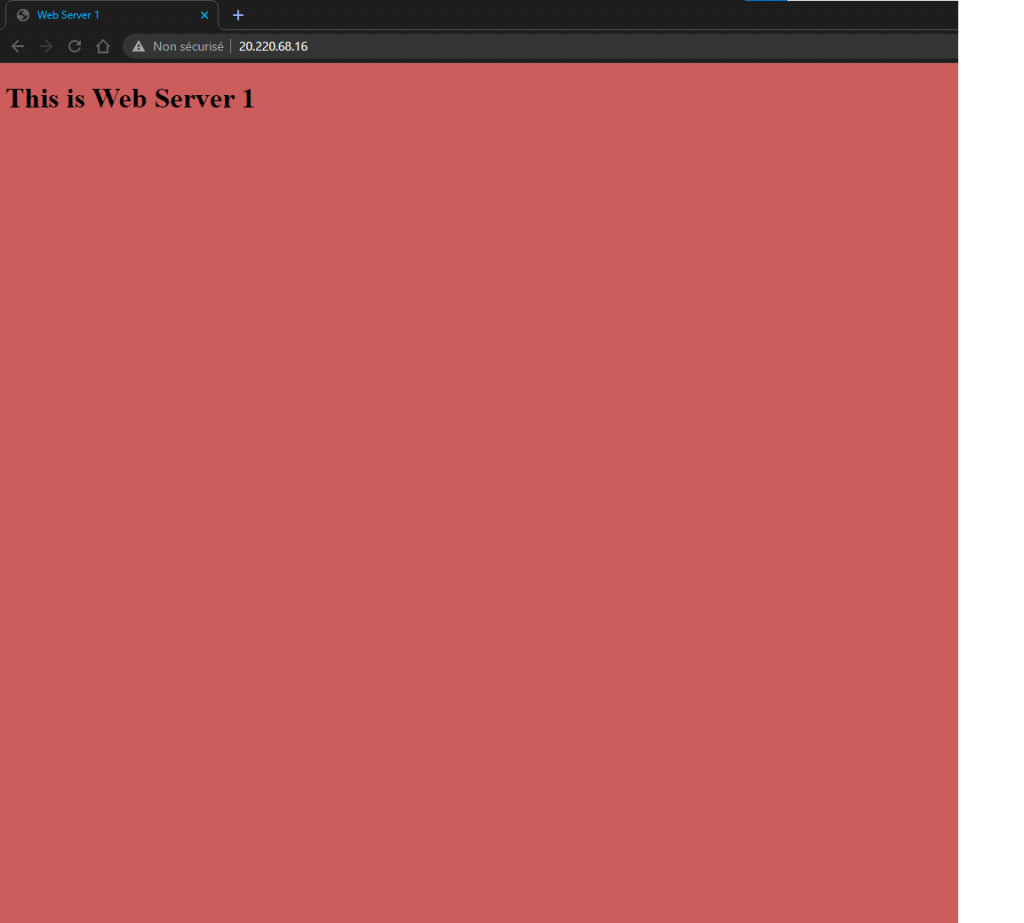
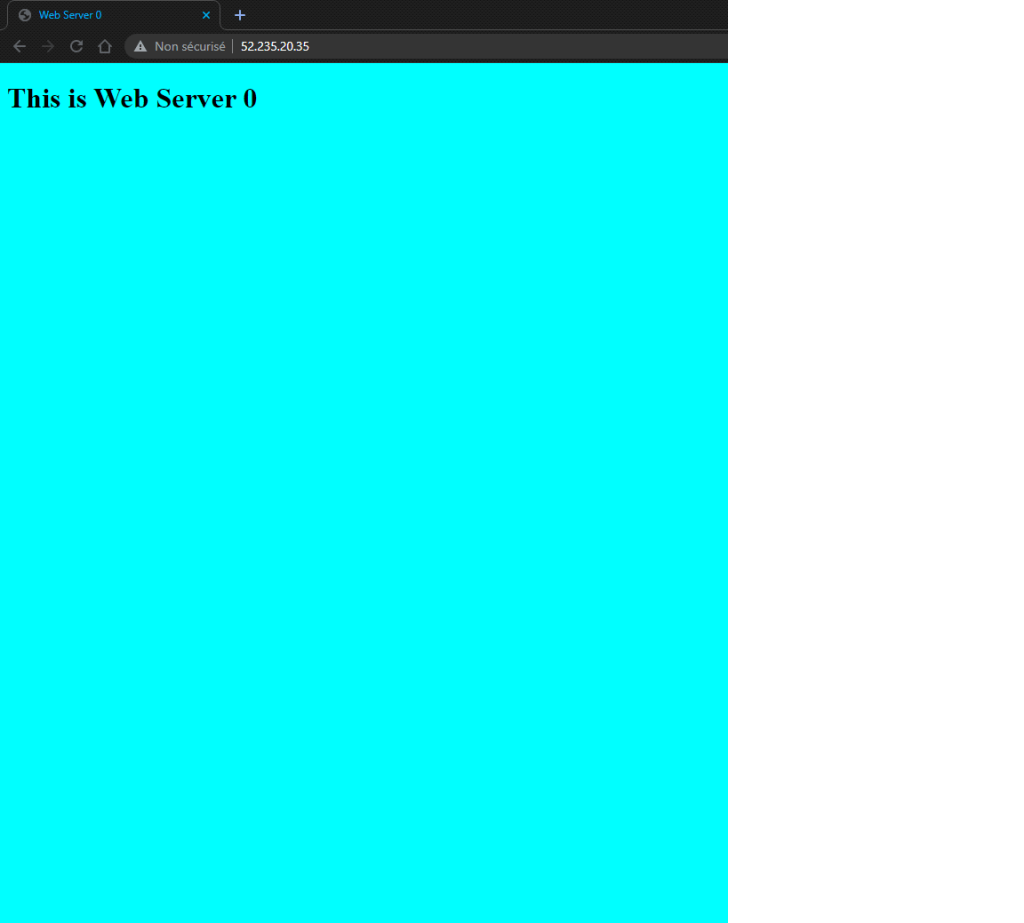
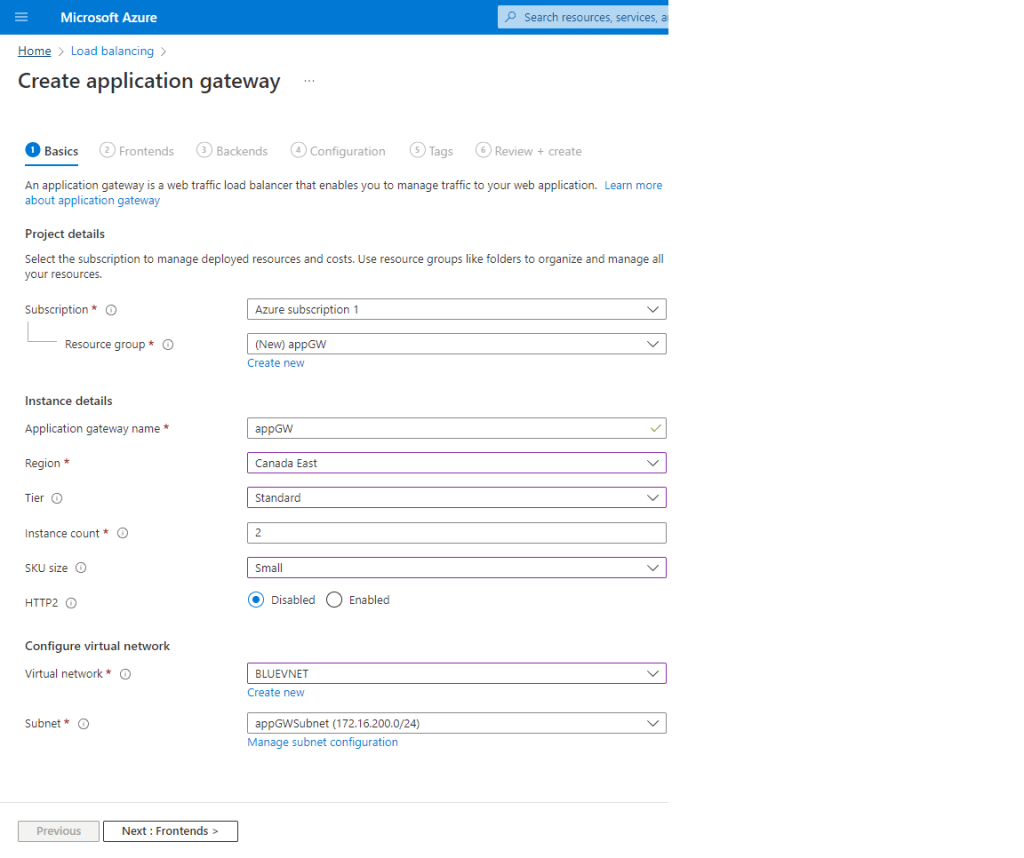
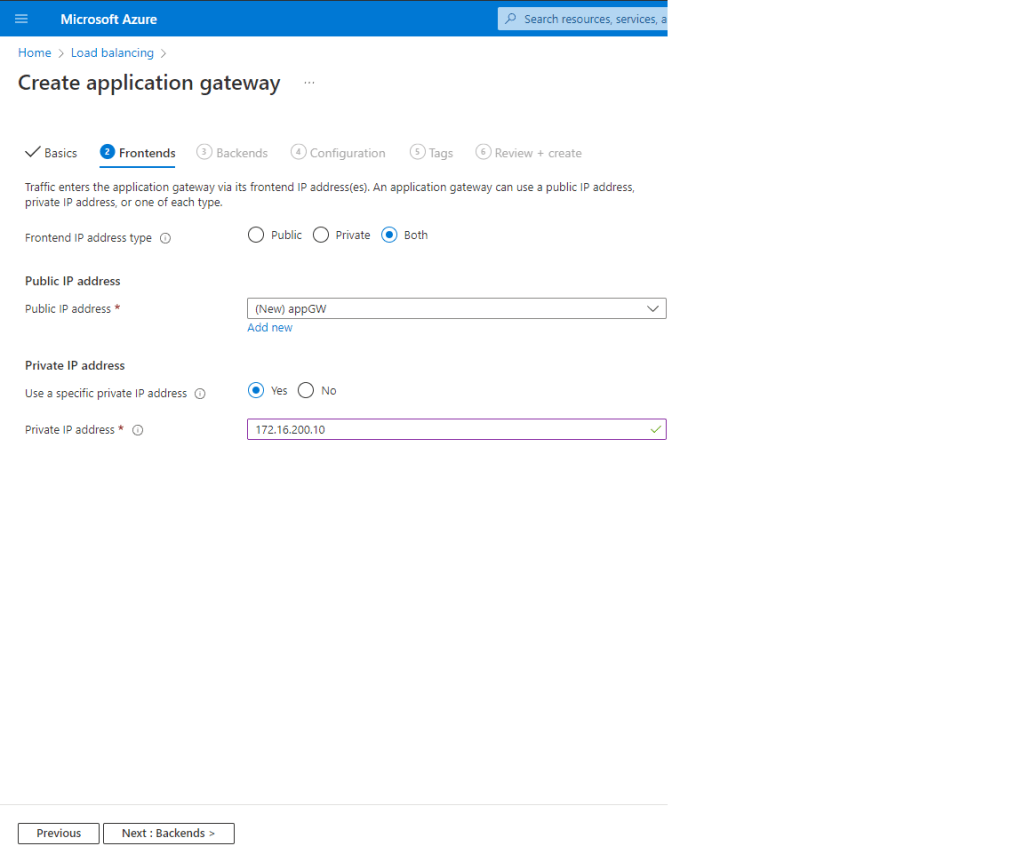
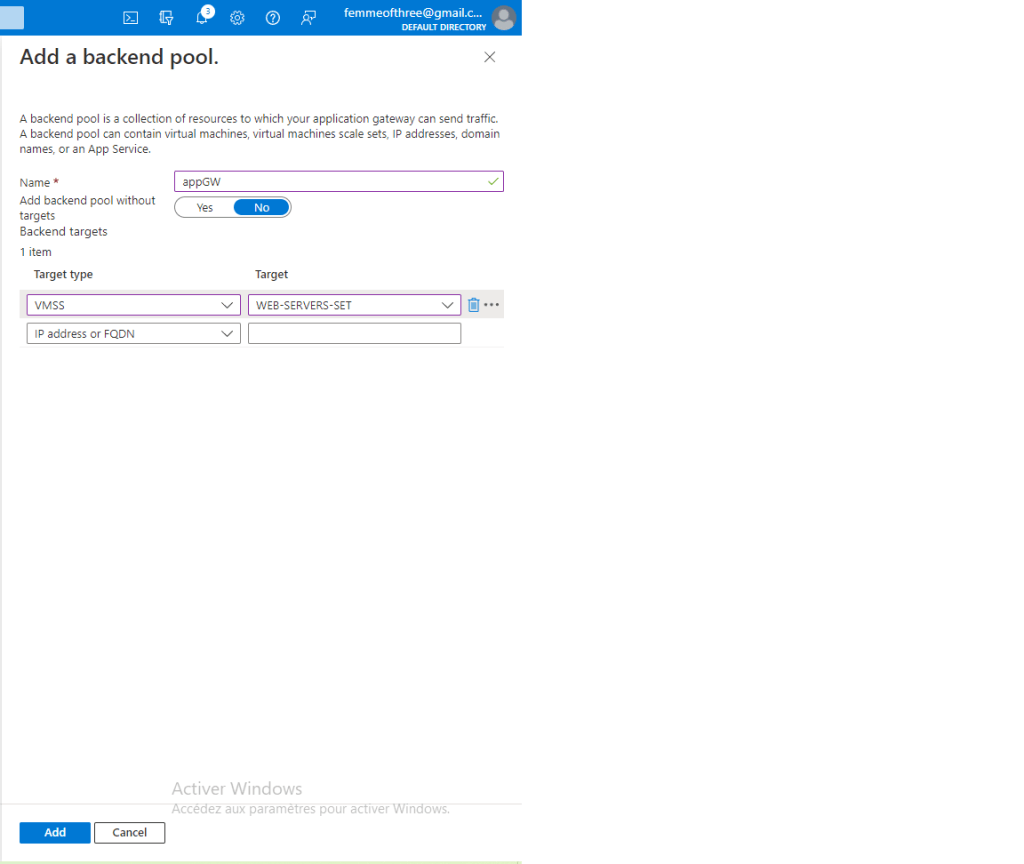
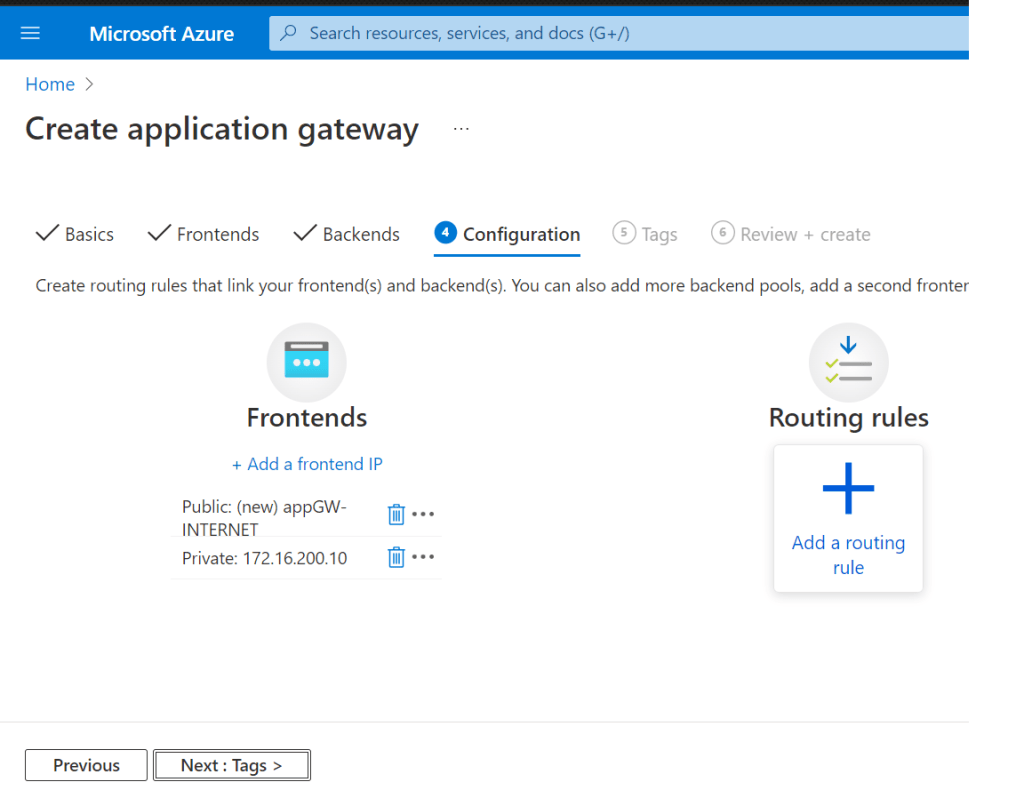
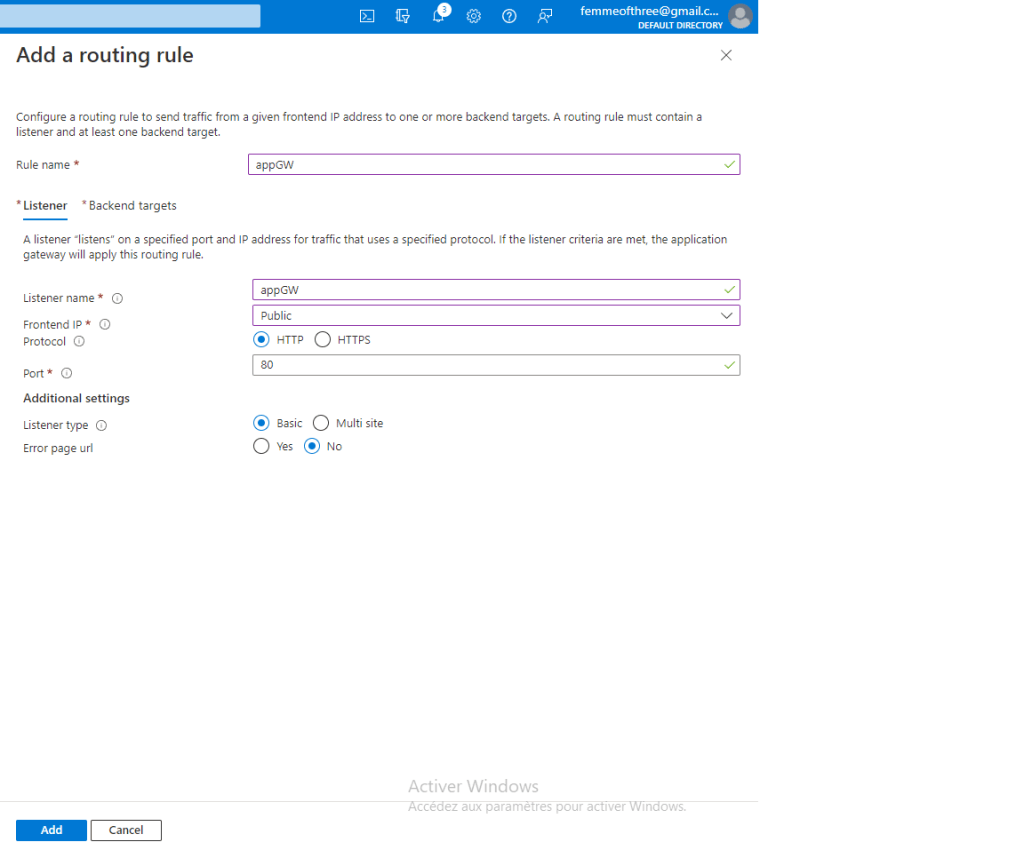
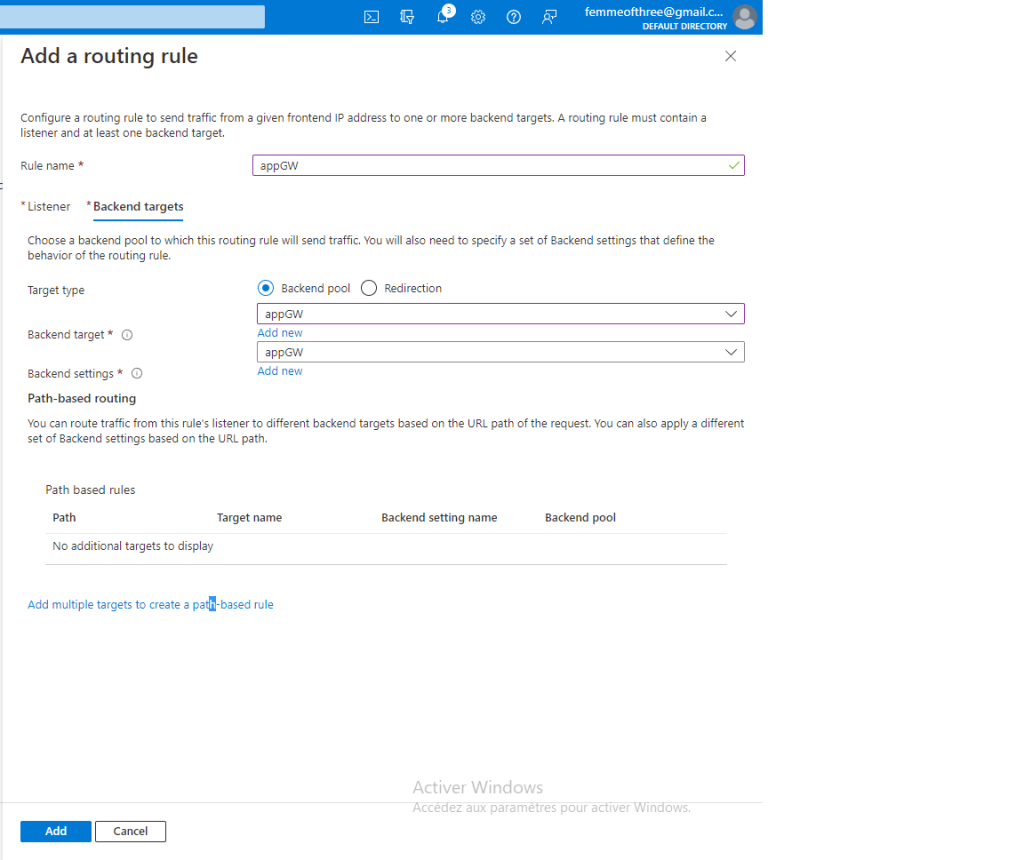
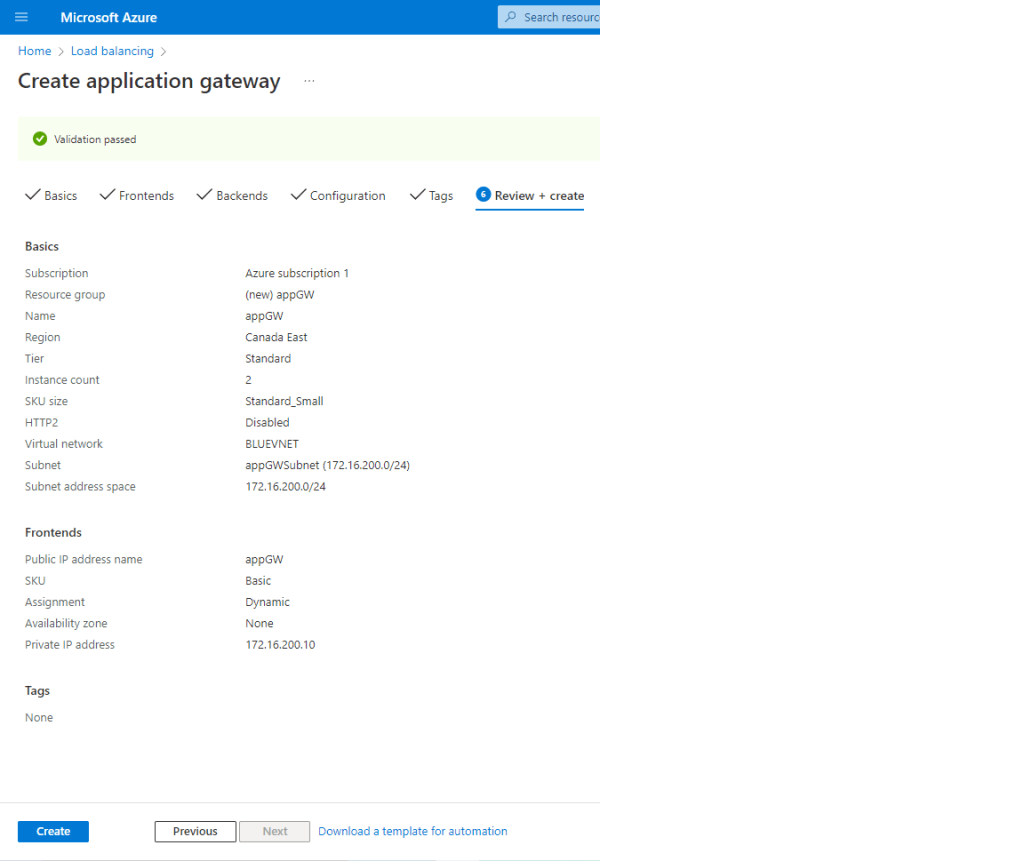
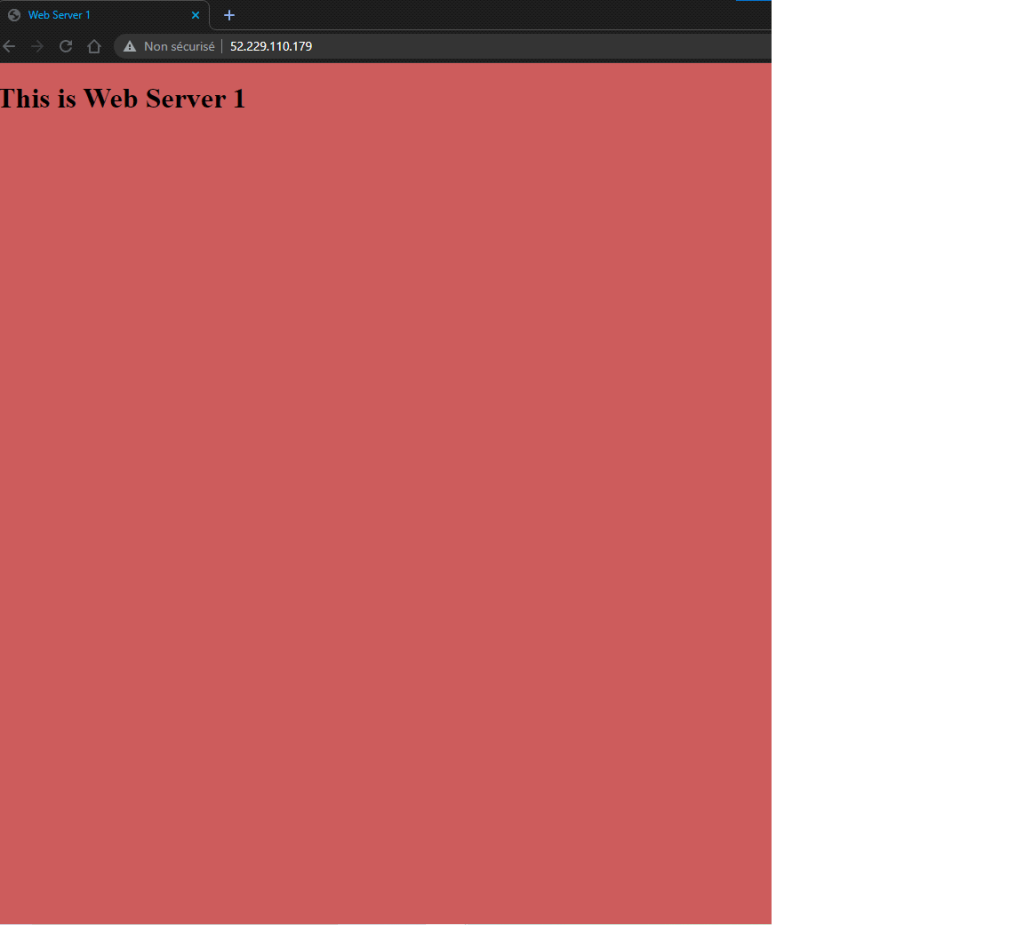
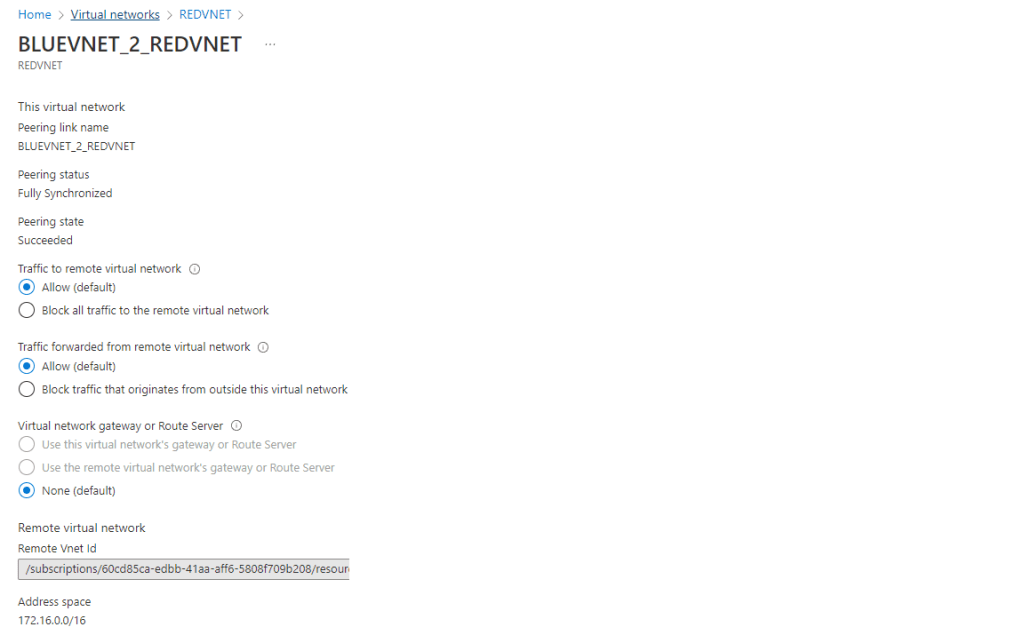
This is a summary of the tasks that have been performed and executed for the previously mentioned customer. 5 cameras were installed on 1 floor and 6 cables were pulled around the office.
- Route the CAT5e patch cable through the hanging ceiling and terminate the RJ-45 end following T568A standard

- Use a washer and a nut to secure the bullet camera to the ceiling tile, without damaging the asthetics